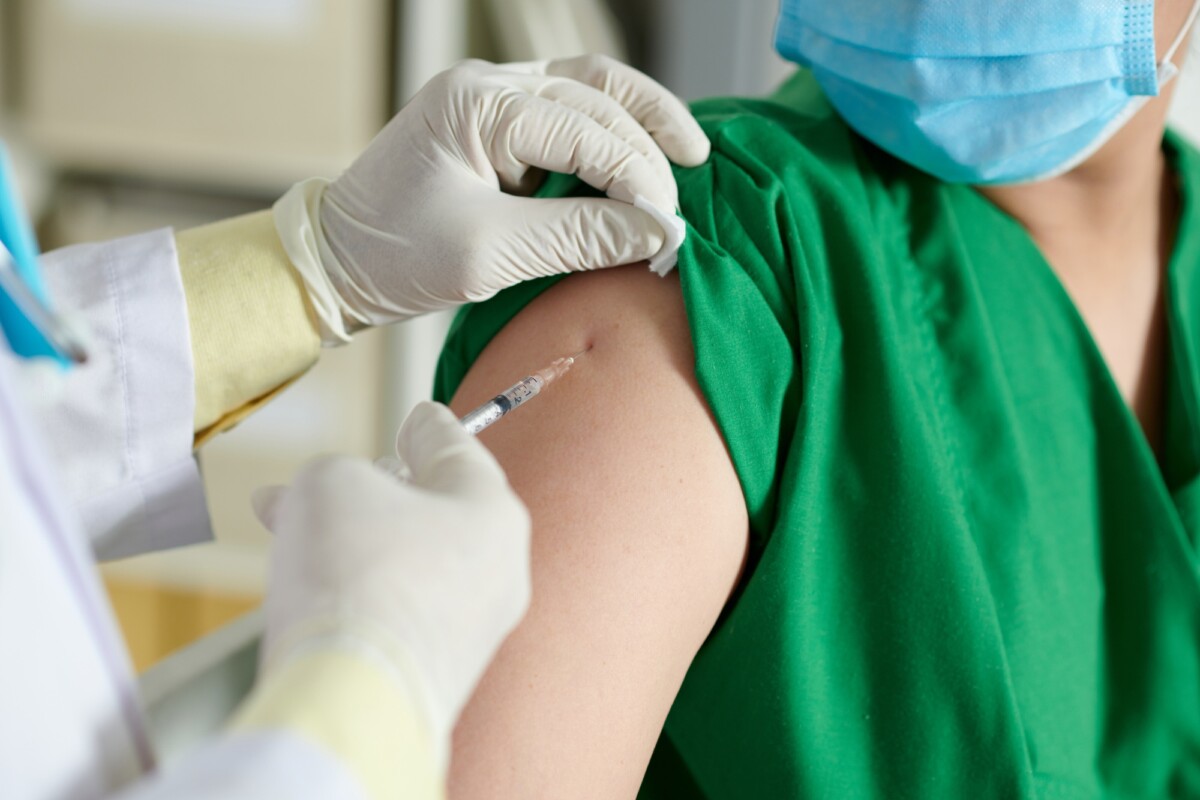
Understanding Prolia Injection for Osteoporosis Management
Prolia injection is a medication that plays a crucial role in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women and individuals at high risk for fractures. This injectable treatment is designed to help strengthen bones and reduce the likelihood of fractures, making it a significant option for those dealing with bone density issues.
What is Prolia Injection?
Prolia injection is a brand name for denosumab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits bone resorption. It is administered subcutaneously, typically once every six months, and works by targeting a specific protein involved in the regulation of bone metabolism. By doing so, Prolia helps to increase bone density and decrease the risk of fractures in patients with osteoporosis.
How Does Prolia Work?
- Inhibits RANKL: Prolia works by inhibiting RANKL (Receptor Activator of Nuclear factor Kappa-Β Ligand), a protein that promotes the formation and activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption.
- Increases Bone Density: Clinical studies have shown that Prolia can significantly increase bone mineral density in the spine, hip, and other skeletal sites.
- Reduces Fracture Risk: According to research, Prolia has been shown to reduce the risk of vertebral, hip, and non-vertebral fractures by up to 68% in high-risk populations.
Who Should Consider Prolia Injection?
- Postmenopausal Women: Especially those with a history of fractures or low bone density.
- Men with Osteoporosis: Particularly those who are at high risk for fractures.
- Individuals on Long-term Corticosteroids: Those who may experience bone loss due to prolonged use of corticosteroids.
- Patients with Certain Medical Conditions: Such as cancer or other diseases that affect bone health.
Prolia injection is not suitable for everyone, and it is essential for patients to discuss their medical history and any potential risks with their healthcare provider before starting treatment. Overall, Prolia represents a significant advancement in osteoporosis management, providing hope for many individuals looking to improve their bone health and reduce fracture risk.
How Prolia Injection Works
Prolia injection is a medication that plays a crucial role in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women and individuals at high risk for fractures. This injectable treatment is significant because it helps strengthen bones and reduce the likelihood of fractures, which can lead to serious health complications. Understanding how Prolia works can empower patients to make informed decisions about their bone health.
Mechanism of Action
- Prolia (denosumab) is a monoclonal antibody that targets RANKL, a protein essential for the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption.
- By inhibiting RANKL, Prolia effectively reduces the activity of osteoclasts, leading to decreased bone loss and increased bone density.
- This action helps to maintain a healthier balance between bone resorption and bone formation, which is crucial for preventing osteoporosis-related fractures.
Administration and Dosage
- Prolia injection is administered subcutaneously, typically once every six months.
- It is important for patients to adhere to this schedule to maximize the benefits of the treatment.
- Healthcare providers may recommend calcium and vitamin D supplements to support bone health during treatment with Prolia.
Efficacy and Statistics
- Clinical studies have shown that Prolia can reduce the risk of vertebral fractures by 68% and hip fractures by 40%.
- In a study involving postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, those treated with Prolia experienced significant increases in bone mineral density compared to those receiving a placebo.
- These statistics highlight the effectiveness of Prolia injection in improving bone health and reducing fracture risk.
Benefits of Prolia Injection
Prolia injection is a medication that plays a crucial role in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women and men at high risk for fractures. This injectable treatment helps to strengthen bones and reduce the likelihood of fractures, making it a significant option for those at risk. Understanding the benefits of Prolia can empower patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions about osteoporosis management.
Strengthens Bone Density
- Prolia injection works by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption. This leads to an increase in bone density, which is vital for reducing fracture risk.
- Clinical studies have shown that patients receiving Prolia experienced a significant increase in bone mineral density (BMD) at the lumbar spine and hip after just one year of treatment.
- According to research, Prolia can reduce the risk of vertebral fractures by up to 68% and hip fractures by 40%.
Convenient Administration
- Prolia is administered as a subcutaneous injection once every six months, making it a convenient option for patients who may struggle with daily medications.
- This biannual schedule allows patients to maintain their treatment regimen without the hassle of daily pills, which can improve adherence and overall treatment outcomes.
- Many patients appreciate the ease of receiving the injection in a healthcare setting or even at home with proper training.
Long-Term Efficacy
- Prolia has been shown to provide long-term benefits in maintaining bone health. Studies indicate that the effects of the injection can last well beyond the administration period, continuing to protect against fractures.
- The ongoing research into the long-term effects of Prolia suggests that it may be a viable option for chronic management of osteoporosis, allowing patients to maintain their quality of life as they age.
- With continued use, patients can expect sustained improvements in bone density and a lower risk of fractures, making Prolia a valuable part of their osteoporosis treatment plan.
Potential Side Effects of Prolia Injection
Prolia injection is a medication primarily used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and men at high risk for fractures. It works by inhibiting bone resorption, thereby increasing bone density and reducing the likelihood of fractures. While Prolia can be highly effective, it’s essential to be aware of its potential side effects to make informed decisions about your health.
When considering Prolia injection, it’s crucial to understand that, like any medication, it may come with side effects. While many patients tolerate the injection well, some may experience adverse reactions that warrant attention.
Common Side Effects
- Back pain: Some patients report experiencing back pain after receiving the injection.
- Muscle pain: Muscle aches can occur, which may be bothersome but typically resolve over time.
- Injection site reactions: Redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site are common and usually mild.
These side effects are generally not severe and can often be managed with over-the-counter pain relief. However, if they persist or worsen, it’s advisable to consult your healthcare provider.
Serious Side Effects
- Hypocalcemia: Low calcium levels can occur, leading to symptoms like muscle spasms or numbness.
- Infections: Prolia may increase the risk of serious infections, particularly in patients with compromised immune systems.
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw: This rare but serious condition involves the death of jawbone tissue and can occur spontaneously or after dental procedures.
It’s important to monitor for these serious side effects and report any unusual symptoms to your doctor immediately. According to clinical studies, the incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw in patients receiving Prolia is low, but awareness is key to prevention.
Long-term Considerations
- Bone fractures: While Prolia is designed to reduce fractures, some patients may experience atypical femur fractures, particularly with long-term use.
- Allergic reactions: Though rare, some individuals may experience severe allergic reactions, including difficulty breathing or swelling of the face and throat.
Patients should have regular follow-ups with their healthcare provider to monitor for these potential side effects and adjust treatment as necessary. Understanding the risks associated with Prolia injection can empower patients to make informed choices about their osteoporosis management.
Who Should Consider Prolia Injection?
Prolia injection is a medication that plays a crucial role in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in individuals at high risk for fractures. This injectable treatment is designed to strengthen bones and reduce the likelihood of breaks, making it a significant option for those who may be vulnerable due to age, gender, or other health factors.
When it comes to deciding if Prolia injection is the right choice for you, several factors come into play. Understanding your personal health history and risk factors is essential. Here are some key groups of people who might benefit from this treatment:
Individuals with Osteoporosis
- Women over the age of 50, especially postmenopausal women, are at a higher risk for osteoporosis due to decreased estrogen levels.
- Men over the age of 70 or those with risk factors for osteoporosis should also consider this treatment.
- Those who have experienced a previous fracture due to low bone density may find Prolia beneficial in preventing future fractures.
Patients with Certain Medical Conditions
- Individuals with conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis or chronic kidney disease may have an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- People taking long-term corticosteroids are also at risk and should discuss Prolia injection with their healthcare provider.
- If you have a family history of osteoporosis, it’s worth considering this treatment as a preventive measure.
Postmenopausal Women
- Statistics show that about 1 in 2 women over 50 will experience a fracture due to osteoporosis in their lifetime.
- Prolia can significantly reduce the risk of fractures in this demographic, making it a vital option for many.
- Women who have not responded well to other osteoporosis treatments may find Prolia to be an effective alternative.
Administration and Dosage of Prolia Injection
Prolia injection is a medication that plays a crucial role in the management of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women and men at high risk for fractures. This injectable treatment helps to strengthen bones and reduce the likelihood of fractures, making it a significant option for those dealing with bone density issues. Understanding how to administer Prolia and the recommended dosage properly is essential for maximizing its benefits and ensuring patient safety.
How is Prolia Administered?
Prolia is administered as a subcutaneous injection, which means it is injected into the fatty tissue just under the skin. Here are some key points regarding its administration:
- Frequency: Prolia is typically given once every six months.
- Location: Common injection sites include the thigh, abdomen, or upper arm.
- Healthcare Provider: While patients can learn to self-administer Prolia, it is often recommended to have a healthcare provider administer the first dose to ensure proper technique.
Preparation for Injection
Before administering the Prolia injection, consider the following:
- Storage: Keep Prolia in the refrigerator until it is time for use. It can be taken out and allowed to reach room temperature before injection.
- Check the Solution: Always inspect the solution for any discoloration or particles before use. If anything seems off, do not use it and consult a healthcare provider.
Dosage of Prolia Injection
Recommended Dosage
The standard dosage of Prolia is 60 mg, administered as a single subcutaneous injection once every six months. Here are some important dosage considerations:
- Individual Assessment: Dosage may vary based on individual health conditions and risk factors. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
- Missed Dose: If a dose is missed, it should be administered as soon as possible. However, if it is close to the time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and continue with the regular schedule. Do not double up on doses.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and to check for any potential side effects. Patients should be aware of:
- Bone Density Tests: These tests may be conducted periodically to assess the effectiveness of Prolia in improving bone density.
- Side Effects: Common side effects may include back pain, pain in the extremities, and elevated cholesterol levels. Always report any unusual symptoms to a healthcare provider promptly.
Recent Studies and Statistics on Prolia Injection
Prolia injection, also known as denosumab, is a medication primarily used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and to prevent bone fractures in patients with certain types of cancer. Its significance lies in its ability to reduce the risk of fractures by inhibiting bone resorption, making it a crucial option for individuals at high risk of osteoporosis-related fractures. Recent studies have shed light on the effectiveness and safety of Prolia, providing valuable insights into its role in bone health management.
Research on Prolia injection has expanded significantly in recent years, revealing promising results regarding its efficacy and safety profile. Several clinical trials have demonstrated its effectiveness in increasing bone mineral density and reducing fracture risk among various populations.
Efficacy in Osteoporosis Treatment
- A study published in the New England Journal of Medicine found that Prolia injection reduced the risk of vertebral fractures by 68% compared to a placebo.
- Another trial indicated that patients receiving Prolia experienced a significant increase in bone mineral density at the lumbar spine and hip after just one year of treatment.
These findings highlight Prolia’s role as a powerful tool in osteoporosis management, particularly for those who may not tolerate traditional therapies.
Safety and Side Effects
- Clinical data suggests that the most common side effects of Prolia injection include back pain, high cholesterol levels, and skin reactions.
- Although rare, serious side effects can include infections and osteonecrosis of the jaw, prompting healthcare providers to monitor patients closely.
Understanding the safety profile of Prolia is essential for both patients and healthcare professionals, ensuring informed decisions regarding osteoporosis treatment.
Statistics on Prolia Usage
- According to recent statistics, approximately 1.5 million Americans are treated with Prolia injection annually, reflecting its growing acceptance in clinical practice.
- The medication has shown a 90% adherence rate among patients, indicating a strong commitment to ongoing treatment and management of osteoporosis.
These statistics underscore the importance of Prolia in the landscape of osteoporosis therapies, showcasing its effectiveness and the trust patients place in this treatment option.
FAQs About Prolia
1. What is the downside of taking Prolia?
While Prolia is effective in treating osteoporosis, it has some potential downsides. Common side effects include back pain, muscle pain, and joint pain. More serious risks include low calcium levels (hypocalcemia), an increased risk of infections, and delayed healing of fractures. Additionally, stopping Prolia without transitioning to another osteoporosis treatment can increase the risk of bone fractures.
2. What does Prolia injection do for you?
Prolia is an FDA-approved medication that helps strengthen bones by slowing bone loss. It is commonly prescribed for individuals with osteoporosis or those at high risk of fractures. The injection works by inhibiting the activity of osteoclasts (cells that break down bone), leading to increased bone density and a reduced risk of fractures in areas like the spine, hips, and wrists.
3. What does Prolia do to your teeth?
Prolia can affect oral health, particularly increasing the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), a rare but serious condition where the jawbone does not heal properly after dental procedures such as extractions. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene, have regular dental checkups, and inform your dentist if you are receiving Prolia treatment to minimize risks.
4. Which is better, Prolia or Reclast?
Both Prolia and Reclast are used to treat osteoporosis, but they work differently.
- Prolia (Denosumab) is an injection given every six months and works by blocking bone breakdown. It is often recommended for patients who cannot tolerate bisphosphonates.
- Reclast (Zoledronic Acid) is a bisphosphonate given as an annual intravenous infusion. It helps slow bone loss and is generally preferred for those who want a once-a-year treatment.
Your Medicare plan should work for you! Find the best fit at NewMedicare.com or dial 📞 (833) 203-6742.